September 4, 2025
Category: E-Commerce
Tinder Business Model: How Does Tinder Make Money?
Tinder does more than connect people – it stands as a profitable consumer subscription product. Its method for pricing, loops for growth along with system for getting money have turned a simple matching tool into a business that makes many billions of dollars. This business always converts engagement into cash flow. If one studies platform economics or builds a social marketplace, understanding how Tinder revenue provides a good lesson in modern product monetization.
Before a deep look, two terms appear often – tinder revenue but also tinder net worth. Tinder revenue refers to the money the app generates from subscriptions, individual features in addition to ads. Tinder net worth is more complex. Tinder is a part of Match Group, so it does not publish a separate, tradable valuation. The brand’s contribution to Match’s market value and cash flow is very big.
If one explores how to build a similar product, a detailed guide on Tinder clone apps offers more. Bold moves, constant tests next to distinct pricing make Tinder a case study in how to get money from attention without completely sacrificing what users experience. The company mixes freemium use with power tools for the most serious users. It then adds periodic, time bound microtransactions to get maximum demand.
Unlock the secrets behind monetizing apps like Tinder!
Talk to an expert now for tailored strategies.
What Tinder Is
Tinder is a dating app that uses location – it made the swipe interface popular to simplify finding people. Users see profile cards of nearby people; they swipe right to like or left to pass. When two people like each other, it is a match and a chat opens. Under the surface, Tinder uses ranking algorithms to order profiles. It balances visibility to keep people engaged across groups – it implements strong safety features, such as photo verification, to keep trust. Over time, Tinder moved from just matching to a system of features – Top Picks, Super Likes, Boosts, subscription tiers that promise more control, visibility, or priority.
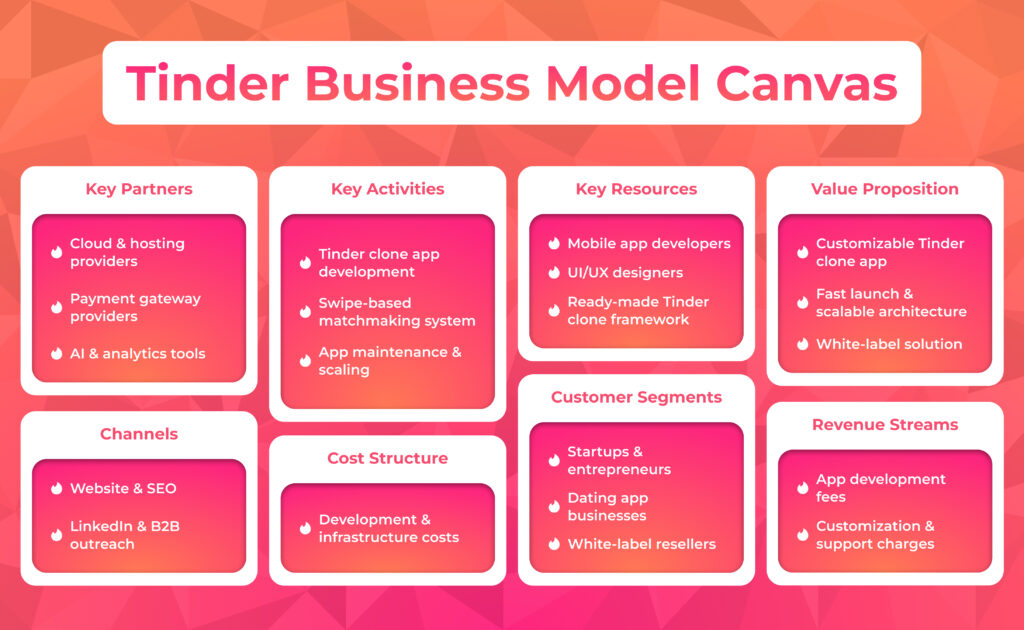
Tinder’s Business Model
At its basic level, Tinder runs a freemium model with three ways to get money
- Subscriptions with different levels of value (Plus, Gold, Platinum) get money from frequent and serious users.
- Individual purchases (Boosts, Super Boosts, Super Likes, priority messages) get money from short term increases in willingness to pay.
- Advertising and brand partnerships get money from free users and add more average revenue per user without needing a paywall.
The system works because of close feedback loops
- Engagement provides data. Data improves ranking and recommendations. Better matches cause people to keep using the app.
- Keeping users increases chances to sell more subscriptions and individual products.
- Premium visibility causes creators of good profiles to spend more for exposure – this improves the marketplace experience.
From an economics viewpoint, Tinder uses price discrimination through tiers, locations along with changeable offers. It targets distinct groups with different willingness-to-pay, such as college users, city professionals in addition to power users, with different packages and time-limited promotions. That spreads how it gets money across groups without forcing a single price on everyone.
Revenue Streams (Plus, Gold, Platinum, Boosts, Ads, etc.)Tinder’s revenue system contains a mix of recurring subscriptions and microtransactions that occur just when needed, with advertising added. Below are the main streams and how they function together.
Subscriptions
- Tinder Plus – This removes ads, offers unlimited Likes, one free Boost per month, and Passport to swipe in other locations – it is the first paid experience, good for frequent swipers who want more volume and control.
- Tinder Gold – This adds daily Top Picks and the ability to see who liked you before you swipe; this truly reduces search time. This level converts users who value speed over looking around.
- Tinder Platinum – This offers Priority Likes and messaging someone before matching with a Super Like – this puts paying users closer to the top of recommendation queues. It is for serious users who value speed and visibility.
Individual Purchases
- Boosts besides Super Boosts – The temporarily place a profile at the top of the deck in a user’s area for a set time. Super Boosts last longer and provide more views. They often find use during busy hours or weekends.
- Super Likes – This signals higher intent and increases the chance of a match – they are sold in packs to cause repeated buying.
- Priority or pay-per-message additions – The are limited, specific features that give visibility or open a conversation window. They are for serious situations.
Advertising and Partnerships
- In-feed native ads and branded experiences – The are campaigns designed to blend with profile cards or interactive formats.
- Category partnerships – The include entertainment launches, event promotions next to nightlife integrations, which get money from attention without requiring users to buy.
Experiments and Add-ons
- In-app currency trials – Coins or credits for flexible buying of Boosts or Super Likes are tested in some markets. That allows for finer price detail.
- Premium verification – This offers better trust signals and richer profile elements as upsell features.
How the revenue layers interact
- Subscriptions get money from repeated use and provide stable average revenue per user.
- Individual purchases get money from purchase intent that occurs at a moment.
- Ads get money from free users with very little difficulty.
Comparison Table – Tinder Monetization Options
| Offer | Core Value | Typical Use Case | Pricing Tendency | Revenue Role |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tinder Plus | Remove ads, unlimited Likes, Passport | Heavy daily users | Entry-tier monthly | Recurring base |
| Tinder Gold | See who liked you, Top Picks | Efficiency seekers | Mid-tier monthly | ARPU lift |
| Tinder Platinum | Priority Likes, message before match | High-intent users | Top-tier monthly | Premium ARPU |
| Boost | Temporary top placement | Peak-time visibility | Per-use microtransaction | Demand capture |
| Super Boost | Extended top placement | Weekends and events | Higher per use | High-margin spikes |
| Super Likes | High-intent signal | Niche targeting | Pack-based | Add-on revenue |
| Ads | Native in feed branding | Monetize free users | CPM/CPC | Incremental ARPU |
As per Match Group filings, tinder revenue has generated roughly around a multi-billion-dollar amount in annual revenue in recent years. Exact amounts vary year to year and because of currency fluctuations. One should always consult the latest investor reports for precise numbers.
Smart Monetization Strategies
Clear Revenue Levers- Subscription Plans: Monthly or annual premium memberships with advanced features. Unlock unlimited swipes, advanced filters, and boost your profile.
- In-App Purchases: Includes one-time purchases like Boosts profile, Super Likes, and your profile visibility upgrades/advancements.
- Advertising: Native ads and sponsored profiles without disrupting the user experience.
- Freemium Upsell: Get Free core features from paid access to premium tools.
- White-Label Licensing: One-time or recurring licensing for businesses that are launching their own Tinder-like app. Branded app usage fees.
- Enterprise Customization: Custom development, integrations, and ongoing support packages for scale-ready platforms are provided
- Custom Services: Paid customization & support
Why It Works
In order to balance user engagement and revenue growth while guaranteeing scalability, flexibility, and long-term profitability for startups and organizations, Autviz Solutions creates Tinder-style apps with built-in monetization from day one.Want to boost your online marketplace success?
Book a free consultation for actionable insights today!
Contact UsWhy the Model Works
The company makes money from subscriptions and small purchases, not just by proportionally increasing costs. A freemium plan with clear upgrade moments allows users to experience a main value free; they then find problems, such as very limited likes, long waits for matches, or low visibility. Premium features directly solve the problems. With tiered value ladders, Plus makes problems fewer, Gold provides more information, and Platinum creates priority.
Each step matches a higher willingness to pay. Time-sensitive small purchases, such as Boosts but also Super Boosts, monetize high attention. They match a willingness to pay with times when demand is highest. Through data, prices and offers are set. Dynamic offers, groups of items along with local prices maximize sales while keeping fairness for free users. The company benefits from operational leverage. Subscription revenue grows with a very small extra cost. New features use existing infrastructure plus machine-learning systems. If you build a similar marketplace, study match quality, user numbers by group, and ways to make users pay. For a deeper product analysis and plan, see our resource about a Tinder clone app.
Challenges and CompetitorsEven with good revenue, the market is full but also changes often. Main problems are
- Competition – Bumble, Hinge, Badoo, Grindr in addition to niche apps compete based on brand, safety next to match quality. Some apps are different because they have fewer swipes and more guided prompts. This can reduce people leaving and change how the apps make money.
- Trust as well as safety – Fake profiles, unwanted messages, harassment hurt the marketplace. Tinder puts money into identity checks, content control along with reporting tools. The are ongoing costs.
- User tiredness – Swiping too much can reduce interest over time. Apps fix this with richer ways to find people, such as video, prompts in addition to more profile details, and healthier session routines.
- Platform limits – App store fees and privacy changes, like ATT on iOS, can affect how well new users are found plus how much money the app keeps.
- Rules and price examination – Different prices based on age or location can cause problems in some markets. Following rules and being clear are important.
- Economy – How much people want to spend changes with economic cycles – this can affect how many people pay for tiers or make small purchases.
Competitors such as Bumble make money with similar tiers but also premium features. But Bumble stresses interactions where women message first. Hinge focuses on a “designed to be deleted” idea with paid features that give importance to conversation quality over quantity. Facebook Dating uses social connections but has had problems with how people see it and how much they use it. Tinder net worth and reach still provide benefits of scale. But protecting average revenue per user while making the experience better is a careful balance.
Recent Tinder Updates — Quick Highlights
Key Updates at a Glance- Stronger user verification & safety
- New dating modes beyond simple swiping
- Increased focus on Gen Z engagement
- Smarter use of AI for matching & retention
Future of Tinder
Expect Tinder to keep making the mix of subscriptions, small purchases next to ads better – it will also explore new features that can demand higher prices
- AI-powered matching as well as profile help – Giving advice on photo improvements, profile edits, conversation starters, all made for the other person’s interests, can increase match and reply rates. That creates ways to make money by helping users succeed faster.
- Safety and realness checks – Government ID checks, live face detection along with verified badges grouped into premium tiers can justify higher prices – they also reduce fraud.
- Event-based discovery – Shared events, festivals in addition to nightlife integrations where Boosts besides Super Boosts become boosts tied to a time plus a place.
- Richer media – Voice notes, short videos next to interactive prompts give more ways for people to engage and for premium placement.
- Smarter ad formats – Ads that know the context and use user interest signals without bothering users. The ads could be sold based on results.
- Local product market fits – Price ranges, payment methods, features made for new markets to expand average revenue per user without losing reach.
From a money making view, the big way to make money is very precise price differences. The come through groups of items, streaks, limited time offers along with loyalty perks, all without upsetting free users. If you build a similar product, calculate the long term value of users by group. Then match upgrade prompts to times when users show a clear interest.
Conclusion
Tinder’s business plan shows how to manage a large, two sided market for attention with accuracy. The free onboarding grows the network, tiered subscriptions monetize continued use, but also timed small purchases capture peak interest. Advertising adds more money without blocking off the main value.
The result is resilient revenue and a brand whose economic contribution to its parent company helps fund continued spending. While tinder net worth is not published, the app’s revenue size and profit margins mean it is a large lasting business. Whether you analyze platforms or build your own, focus on user numbers by group, clear value steps in addition to selling that respects user time as well as trust. Change things often. Packaging next to personalization are ongoing tests, not one time decisions.
Explore more insights at Autviz Solutions.
